The National Library of Medicine discovered that about 30% of US adults use wearable medical devices, such as smartwatches, smart glasses, and other fitness trackers.
This shows how abundant wearables are globally. Although many people still associate wearable technology with tracking fitness, advances in medical technology now allow patients to use it to monitor their health.
As a result, the burden of chronic disease, aging populations, and rising healthcare costs could all be addressed by wearable technology.
GlobalData estimates that the market for wearable technology was worth nearly $27 billion in 2019 and will grow by 24.6% annually between 2020 and 2024 to reach $156 billion.
What Does Wearable Technology Mean in the Medical Field?
In its simplest form, “wearables” refers to Internet of Things (IoT) solutions that integrate hardware, software, and app development.
For example, in healthcare, personal health data is collected, transmitted, and analyzed using a network of electronic devices—typically worn by patients—and user interfaces—often mobile applications—connected to the cloud.
Smart sensors built into these devices enable the measurement and monitoring of critical physiological characteristics, including heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
Of course, other medical IoT devices like wearables or ingestible can also collect this data in addition to others. But up until now, wearable medical technology has been the most well-liked.
Despite what you might initially think, wearables are much more than fitness trackers. They are often tiny enough to wear as a wristband or patch and intelligent enough to manage chronic illnesses and avoid severe sickness.
Types of Medical Wearable device
We’ll focus on the readily available devices right now, even though the technology is constantly developing and new products are being introduced.
These include consumer electronics purchased by the general public and high-quality medical products utilized by healthcare specialists.
Wearable Fitness Trackers
![]()
These are among the simplest wearable technologies enabling users to monitor such fundamental characteristics as a heart or pulse rate to monitor their health.
The wristbands also aid in regulating physical activity and keep track of steps taken, stages of sleep, and calories burned.
These tiny gadgets have sensors and are linked to cell phones. Thanks to mobile app developers creating various user-friendly solutions, people may access and handle acquired data on their mobile phones.
You can count among those who gain from such apps daily.
Smart Health Watches

Smartwatches have been available on the electronic gadget market for a while now. They just lately began to offer actual value in terms of health, though.
Smartwatches can give users information about their levels of physical activity, stress, or even abnormalities in their cardiac patterns, in addition to the ability to manage calls and texts and issue voice instructions.
New developments in optical sensors, semiconductors, AI, and data science technologies have enabled the last to be accomplished.
They all served as the foundation for photoplethysmography, often known as PPG, a measuring technique used to track volumetric fluctuations in blood circulation.
It can be used, for instance, to monitor patients remotely to spot heart disease.
Read Also: The rise of wearable technology: what to expect in 2024
Wearable ECG Monitors
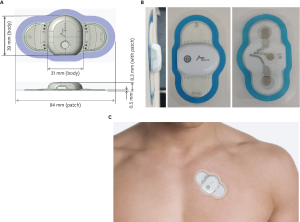
37% of American consumers monitor their heart health with wearable technology. Because of this, the future of ECG monitors is very bright.
This wearable medical gadget aids in treating cardiovascular patients and is used to identify common arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation (AF).
Modern ECG monitors utilize advanced machine learning algorithms to efficiently measure electrocardiograms and identify anomalies.
A doctor can then use the information to perform additional investigations and diagnose symptomatic or asymptomatic AF.
Wearable Blood Pressure Monitors

The ability of hypertension to increase morbidity and death is well-known worldwide. Wearable technology that includes blood pressure (BP) monitors expand the opportunity for regular hypertension screening—in this approach, increasing well-being and improving healthcare delivery.
In this approach, increasing well-being and improving the delivery of healthcare. Due to recent advancements in wearable technology, users may take blood pressure readings discreetly.
Even though this technique is still in its infancy and needs further investigation, monitoring blood pressure without a cuff improves the patient experience and gives medical professionals more resources to address heart diseases.
Biosensors

Biosensors are the final wearable health monitoring technology category we will discuss today. They often use self-adhesive patches with AI-based analytics and sensor development to gather crucial health data without impeding movement.
Patients and medical professionals can assess things like cardiac output, respiration rates, weight, or even fluid volume with the help of biosensors.
Hence raising the likelihood of avoiding cardiac failure. In addition, adopting this non-invasive, ongoing monitoring technique opens the door to better patient outcomes and service delivery.
Wearable Technology: Benefits and Drawbacks
As you can see, various wearable technologies have already attained broad consumer and medical acceptability. What, then, are the causes of this rising demand?
It is no surprise that many businesses are utilizing the advancement of medical wearables because the technology offers the healthcare industry a wealth of chances and advantages.
The participants in the sector typically accomplish the following objectives through the usage of these small devices:
1. Encourage preventative healthcare
With wearable technology, it’s simple to constantly check the health and identify any changes in vital signs as soon as they occur.
As a result, consumers can proactively prevent significant health issues before they become a problem. Additionally, professionals can assist patients in responding rapidly to notifications and administering treatment.
Wearables improve care delivery in this way and promote patient-centricity.
2. Increase Customer Engagement
Wearables give users access to insightful data that empowers them to feel in charge of their health and keep informed about it.
In addition, technology makes it easier for patients and doctors to work together and involves them in ongoing health maintenance.
3. Lower Medical Costs
Patients spend less money on doctor visits because wearables reduce illness risks, improve early diagnosis, and promote health.
On the other hand, medical professionals can monitor patients after they leave the hospital to prevent readmission fees and a reduction in insurance reimbursements. In this manner, technology lowers the cost of healthcare.
4. Reduce Employee Workload
Numerous personal health data points are produced by wearable technology, which can be shared with clinicians and examined to monitor patients remotely.
As a result, the workload of healthcare workers can be reduced, personal visits can be diminished, and communication can be improved using this strategy.
Drawbacks of Medical Wearables
The challenges that wearable gadgets present in the healthcare industry today go along with their advantages. This technology still needs some work because it is so new. Below are the issues medical wearables have:
Technical Problems
In the past, powerful batteries were needed to power portable medical devices. In addition to fitting inside small-sized gadgets, these batteries ought to offer wireless charging to meet consumer expectations.
Therefore, businesses should consider putting money into better semiconductor technology.
Data Reliability
Accurate data is only helpful, and this is especially true for health-related data. Therefore, it should be generated, transported, and processed most effectively because of this. IoT, Big Data, and AI applications may be helpful in this situation.
Privacy and security
Wearable device owners are worried about the security and privacy of shared health information. Companies should implement security standards and abide by privacy policies to protect data during transport and storage, as it is still a barrier.
In addition, make sure your solution complies with HIPAA regulations.
Wearing a device improperly
The placement of wearable sensors significantly impacts the accuracy of measurements and data. They must be positioned correctly and near the skin. Additionally, a tattoo or even wetness can lead to inaccurate readings.
The Healthcare Industry’s Use of Wearable Technology in the Future
Despite all the current obstacles, the number of consumers- and medical-grade wearables will increase over the next few years. As a result, that market segment is still quite lucrative and presents many prospects for improving the healthcare environment.
Patients and clinicians can keep track of a greater spectrum of medical disorders as devices and apps become more intelligent and trustworthy.
In addition, it becomes clear that more businesses will be motivated to create linked devices and software to enable them.
The effectiveness of wearable technologies will be increasingly impacted by the development of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
It can improve measurement accuracy and reduce cybersecurity threats. Furthermore, combining IoT innovations with predictive analytics tools can help increase patient data insights.
Read Also: The digital divide: how technology exacerbates inequality
Conclusion
Patients and healthcare professionals can track health status remotely using continuous glucose monitors (CGM), implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), and non-invasive devices like pulse oximeters.
In addition, wearable technology allows patients to more conveniently monitor their condition with other health parameters like activity monitoring and heart rate. Also, it will enable this data to be accessed via computers or smartphones.
In healthcare, wearable technology devices efficiently collect patient data for data-driven machine-learning algorithms to examine users’ health problems.
For example, vital sign data, including heart rate, blood pressure, and other measurements, can be uploaded to the cloud for real-time analysis and predictive diagnosis, which includes recommending hospitalization if a person’s heartbeat becomes irregular.

